
Vimal Kumar Rai
Managing Partner and Co-Author

AJ Boelens
Managing Partner and Co-Author
How to Build Customer Centricity into Your Business Strategy
This comprehensive guide will delve into what customer centricity truly means, provide examples of organizations excelling in this area, and offer a roadmap for integrating customer centricity into your business strategy.
In the ever-evolving business landscape, placing the customer at the heart of your strategy isn’t just beneficial; it’s imperative for success. Customer centricity, a philosophy where the customer’s needs and experiences are the primary focus of all business decisions, is the key to unlocking sustained growth and competitive advantage.
This comprehensive guide will delve into what customer centricity truly means, provide examples of organizations excelling in this area, and offer a roadmap for integrating customer centricity into your business strategy.
What is Customer Centricity?
At its core, customer centricity is about understanding and responding to the needs and desires of customers. It goes beyond customer service; it’s a business model and a cultural mindset that permeates every department and decision within an organization. A customer-centric company continually gathers and analyzes customer insights to create a superior experience that retains existing customers and attracts new ones. At the same time, we need to identify what customers really value and are willing to pay for.
Examples of Customer-Centric Organizations
1. Salesflare
This CRM software company stands out for making its platform exceptionally user-friendly, thereby addressing a common pain point in the CRM industry. Salesflare’s focus on user experience simplifies customer relationship management for small businesses.
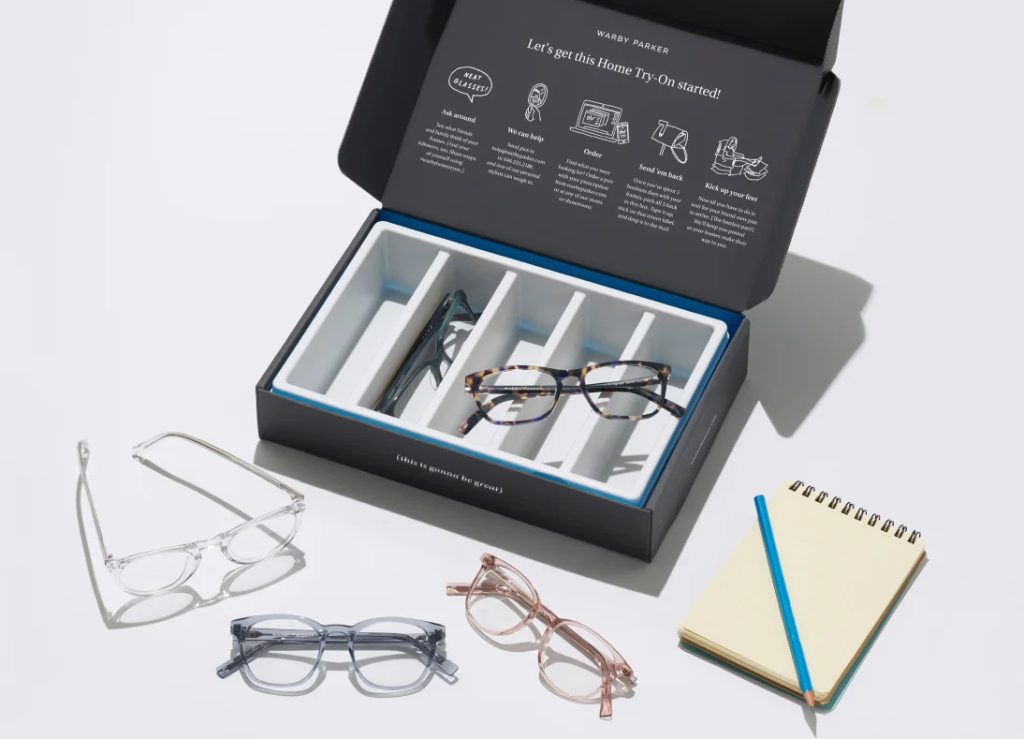
2. Warby Parker
This eyewear company revolutionized the traditional model by offering home try-on services, a user-friendly website, and exceptional customer support. They’ve made buying glasses online as seamless and risk-free as possible.

3. Spotify
The music streaming giant excels in personalization, offering curated playlists and recommendations that resonate with individual user preferences, thus creating a highly personalized listening experience.
Recognizing What Customers Value
Understanding your customers requires more than just surface-level insights. It involves deep research, continual customer feedback loops, and data analytics. Methods like Net Promoter Score (NPS) or Customer Happiness surveys, customer interviews, and social media listening are crucial for gaining nuanced understanding.
Recognizing what customers value is a critical aspect of building a customer-centric strategy. It involves delving into the nuances of customer needs, preferences, and expectations. This understanding forms the basis for tailoring products, services, and experiences to match customer expectations while also understanding willingness-to-pay (WTP).
Key Components in Recognizing Customer Value
1. Understanding Customer Needs
The first step is to identify the core needs of your customers. These needs can be functional, like the need for a cost-effective solution, or emotional, like the desire for prestige or security.
For instance, Tesla understands that its customers value not only sustainable transportation but also innovative technology and status.

2. Analyzing Customer Feedback
Regularly collecting and analyzing feedback through surveys, reviews, and direct interactions provides insights into what customers appreciate or want to be improved.
Starbucks, for example, uses its customer feedback program to gather insights that drive product innovation and service enhancements.

3. Observing Customer Behavior
Tracking how customers interact with your organisation in the marketing and sales funnel as well as through their end-to-end customer journey offers valuable data. This includes engagement levels, purchase patterns, usage data, and online behavior analytics.
Companies like Netflix excel in this aspect by analyzing viewing patterns to recommend personalized content.

4. Engaging in Social Listening
Monitoring social media and online forums helps understand customer sentiment and emerging trends.
Brands like Glossier have leveraged social listening to develop products that resonate with their audience’s desires and preferences.
5. Customer Segmentation
Dividing your customer base into segments based on their needs or jobs to do, behavior, or psychographics helps in tailoring your offerings.
For a B2B example, BASF, the worlds largest chemical company, segments their customers by their jobs-to-do (needs-based segmentation). This has allowed them to better design business interactions models that are suitable for each customer segment.
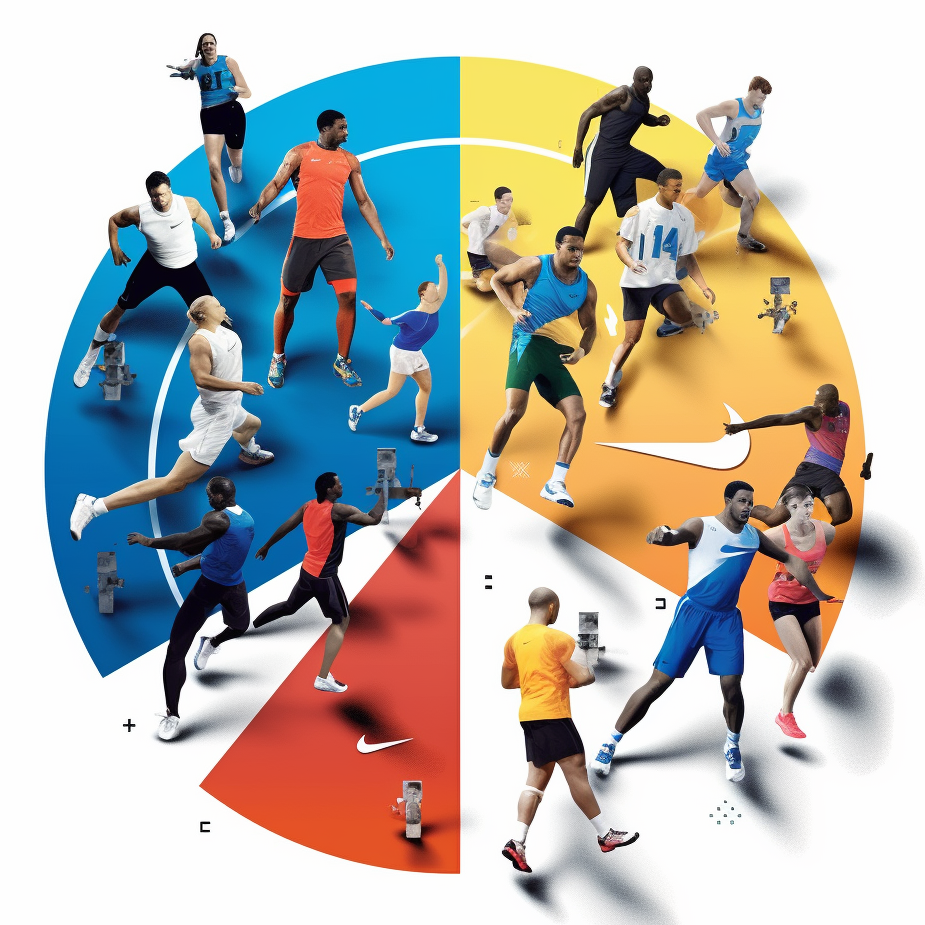
For a B2C example, Nike segments its market into athletes, casual fitness enthusiasts, and fashion-oriented customers (lifestyle based segmentation) creating products and marketing strategies for each group.

6. Benchmarking Against Competitors
Understanding how your offerings stack up against competitors helps in identifying areas for improvement and opportunities to differentiate.
Dyson, for instance, differentiates itself through superior technology and design, addressing customers’ desire for efficient and aesthetically pleasing home appliances.
7. Leveraging Data Analytics
Utilizing data analytics tools to decipher patterns and preferences from customer data can provide a competitive edge.
Amazon excels in this by using customer data to personalize shopping experiences and make product recommendations.

8. Creating a Feedback Loop
Establishing a mechanism to continually gather, analyze, and act on customer feedback ensures that customer value remains a focal point.
Ritz-Carlton‘s legendary customer service is a result of its commitment to continually adapting based on guest feedback.

By recognizing what customers value and integrating these insights into your business strategy, you can build stronger customer relationships, enhance brand loyalty, and drive business growth.
Designing and Delivering Customer Value
Once you understand what your customers value, the next step is integrating these insights into every facet of your business strategy. This process involves:
1. Product Development: Tailoring products and services to meet the specific needs and preferences of your customer base.
2. Customer Experience Design: Ensuring that every interaction with your company is positive, seamless, and reflective of your customers’ values and preferences.
3. Marketing and Communication: Crafting messages and campaigns that resonate with your target audience, based on the insights gathered.
Designing and delivering customer value is an essential process for any business looking to establish a strong, customer-centric model. This process involves creating products and services that not only meet customer needs but also exceed their expectations, thereby offering exceptional value.
Steps in Designing and Delivering Customer Value
Step 1: Understanding Customer Needs and Preferences
Before designing any product or service, it’s crucial to understand what your customers value. This might involve conducting market research, analyzing customer feedback, and monitoring trends.
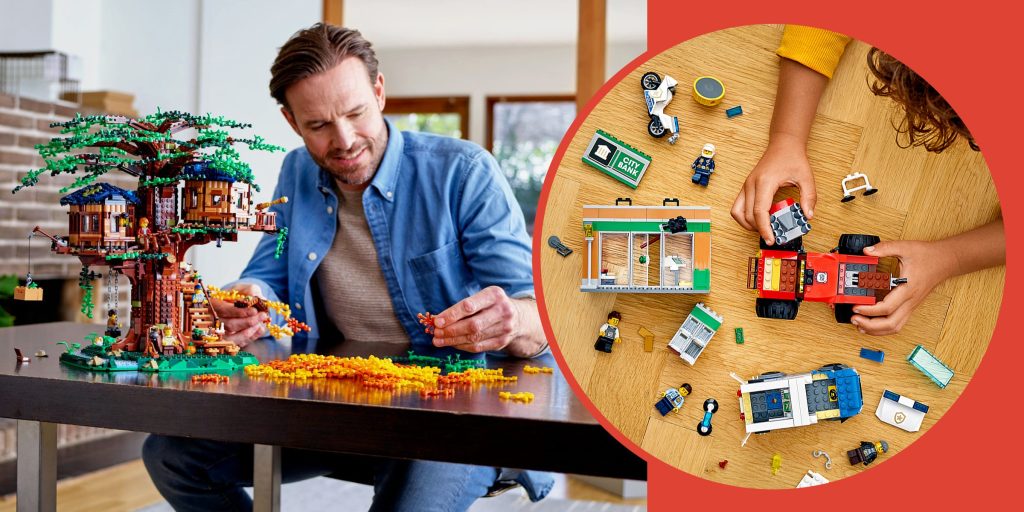
For example, Lego continuously evolves its product lines based on customer interests, incorporating themes and characters that resonate with their target audience.

Step 2: Developing Solutions Aligned with Customer Needs
Once you understand your customers’ needs, the next step is to develop solutions that address these needs. This could mean creating new products, improving existing ones, or offering complementary services.
For instance, Adobe’s transition to a subscription-based model for its software suite was in response to customer preferences for more accessible, up-to-date, and cost-effective software solutions.

Step 3: Evaluating Economic Value to the Customer (EVC)
EVC is a measure of the worth of a product or service to a customer, compared to its alternatives. This involves quantifying the benefits and costs of your product from the customer’s perspective.
McKinsey suggests using EVC as a tool to estimate the economic value customers receive from your products, which can guide pricing and marketing strategies.

Step 4: Effective Communication of Value Propositions
Communicating the value of your products or services effectively is key to delivering customer value. This means highlighting not just the features of a product, but also how it solves customer problems or improves their life.
For instance, Dyson doesn’t just sell vacuums; it sells efficient and innovative solutions to household cleaning challenges.

Step 4: Pricing Strategically
The price of your product or service should reflect the value it provides. Offering a price that makes customers feel they are getting more than they pay for is an effective strategy.
For example, Costco’s business model of bulk purchasing allows it to offer products at lower prices, creating high perceived value for its members.

Step 6: Enhancing the Customer Experience
The overall experience of interacting with your brand, from the first touchpoint to post-purchase support, should reinforce the value proposition.
Companies like Apple excel in this by providing not just innovative products but also an exceptional retail and customer service experience.

Step 7: Continuous Improvement Based on Feedback
To continually deliver customer value, it’s vital to keep the feedback loop open. Regularly collecting and acting on customer feedback helps in improving products and services.
Amazon, for example, continuously evolves its offerings and user experience based on customer feedback and shopping behavior data.

Designing and delivering customer value is an ongoing process that requires constant attention and adaptation. By understanding and aligning with customer needs, communicating effectively, pricing strategically, and continually enhancing the customer experience, businesses can create and sustain high customer value.
Linking Customer Centricity with Business Strategy
Integrating customer centricity into your business strategy requires a shift in mindset, from product-focused to customer-focused. This shift involves:
1. Alignment of Company Culture: Fostering a culture where every employee understands the value of the customer and is empowered to make decisions that enhance the customer experience.
2. Data-Driven Decision Making: Leveraging customer data to guide strategic decisions, from product development to marketing.
3. Continuous Innovation: Regularly updating and improving products, services, and experiences in response to evolving customer needs and feedback.
Linking customer centricity with business strategy is a pivotal move for companies aiming to thrive in competitive markets. This approach involves aligning company goals and processes with the needs and preferences of customers.
Here are some real-world examples of companies that have successfully made this connection:
And here are some examples of companies that have unsuccessfully done so:
Conclusion
In conclusion, the link between customer centricity and business strategy is crucial for long-term success. Companies that listen to and adapt based on customer feedback tend to thrive, while those that fail to do so risk losing relevance in an ever-changing market.
Building customer centricity into your business strategy is not a one-time effort; it’s a continuous journey. It requires commitment, a willingness to adapt, and a culture that prioritizes the customer above all else. By following these guidelines and learning from successful customer-centric companies, you can position your business to thrive in today’s customer-driven marketplace.
This comprehensive guide barely scratches the surface of a complex and nuanced topic. For more in-depth insights and tailored advice, consider consulting with an expert in customer centricity.
Sources:
Chambers, S. (2022, June 21). 6 Customer Centricity Examples To Use In Your Business. Help Scout. https://www.helpscout.com/blog/customer-centricity-examples
Solis, B. (2021, July 22). A Blueprint for Becoming a Customer-Centered Company. Harvard Business Review. https://hbr.org/sponsored/2021/07/a-blueprint-for-becoming-a-customer-centered-company
Woods, K. (2023, January 30). How to make your brand customer-centric (+ top examples). Sprout Social. https://sproutsocial.com/insights/customer-centric/
Gilliland, N. (2019, February 21). Five examples of customer-centric companies. Econsultancy. https://econsultancy.com/examples-customer-centric-companies/
Mukundan, G. (2021, December 12). Brilliant Examples of Companies That Have Built a Customer-Centric Culture (and What You Can Learn From Them). GatherUp. https://gatherup.com/blog/companies-that-have-built-a-customer-centric-culture/
Prochazka, T. (n.d.). 5 Best Customer Centricity Examples That Win Customer Praise and Loyalty. Usersnap. https://usersnap.com/blog/customer-centricity-examples/
